With more devices connecting than ever before, choosing the right wireless setup—2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and properly configured guest networks—can dramatically improve speed, stability, and security. This guide explains the differences between Wi-Fi bands, which devices should use each network, and how businesses and households can build secure, scalable wireless environments that perform consistently.
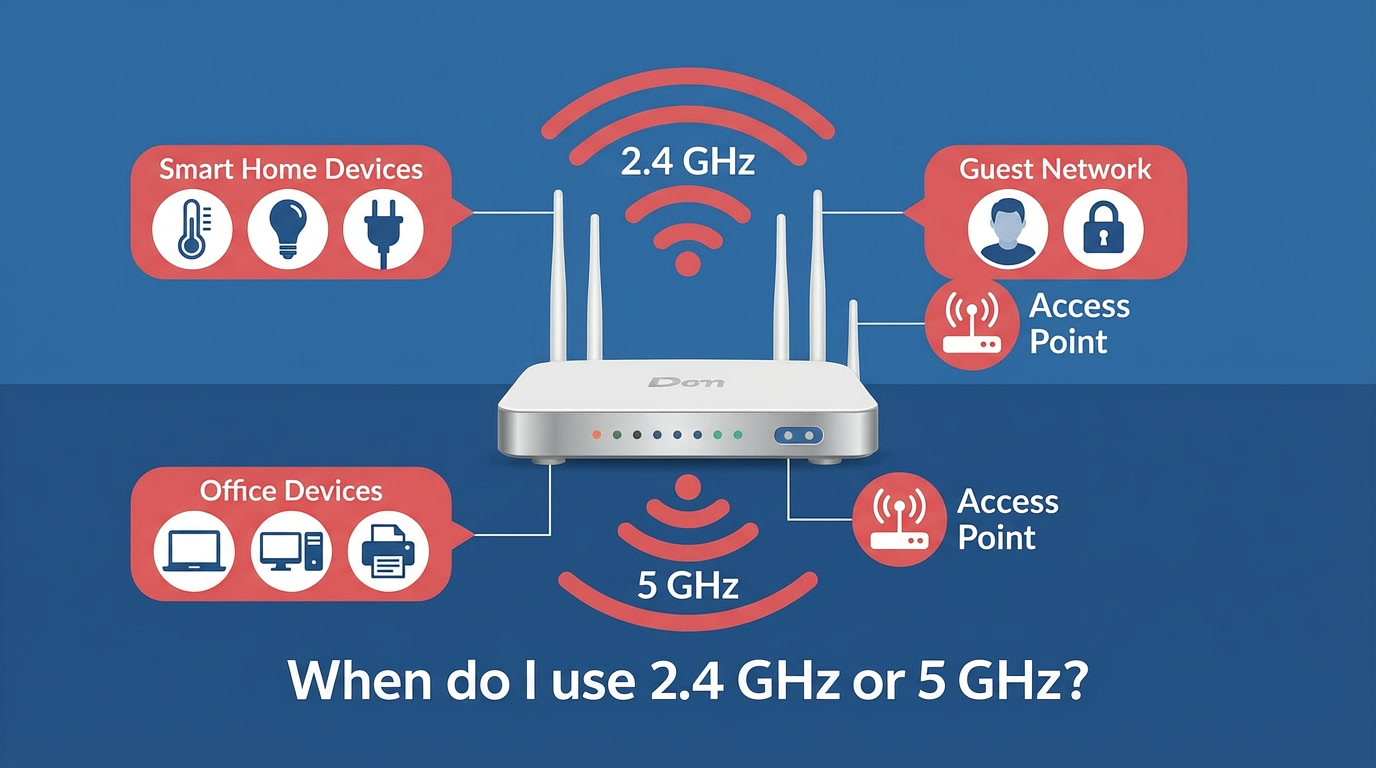
Understanding the Difference Between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi
2.4 GHz Wi-Fi
This band is widely supported and preferred by many IoT devices. It provides:
- Wider coverage and better wall penetration
- Suitable range for outdoor or distant devices
- Lower speeds due to congestion and interference
Common household and commercial devices still rely on 2.4 GHz because it offers superior range despite slower throughput.
5 GHz Wi-Fi
The 5 GHz band provides:
- Higher speeds and lower latency
- Better performance in high-density areas
- Reduced interference from household electronics
This band is ideal for modern devices that require fast, responsive connectivity.
Quick Tip
Think of 2.4 GHz as a country road—slower but reaches farther. 5 GHz is like a motorway—faster but has a shorter range.
Residential Wi-Fi: Which Devices Should Use 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz?
Homes now average between 25 and 50 connected devices, many of which communicate in the background. Using the correct Wi-Fi band for each device prevents congestion and improves performance.
Devices That Should Use 2.4 GHz at Home
Many consumer smart home devices require 2.4 GHz. These include:
- Solar inverters (Fronius, Sungrow, GoodWe, etc.)
- Pool monitoring systems
- Smart lights, switches, and smart plugs
- Robot vacuums
- Smart locks and home sensors
- Older laptops and phones
These devices do not need high speed—they need range and consistent connectivity.
Devices That Should Use 5 GHz at Home
High-speed devices are best on 5 GHz:
- 4K/8K TVs (Netflix, YouTube, streaming services)
- Gaming consoles (PS5, Xbox Series, Nintendo Switch)
- Modern smartphones and tablets
- Laptops for work-from-home
- Video conferencing hardware
- Wi-Fi cameras located near access points
Switching these devices to 5 GHz reduces congestion on the 2.4 GHz band.
Do You Need Additional Access Points or a Dedicated Switch?
As the number of connected devices grows, a single modem/router may no longer be enough. You may require:
- Additional access points
- A mesh Wi-Fi system
- A PoE switch for wired stability
- A router that can handle high device density
Important
Most ISP-provided routers cannot sustain dozens of simultaneous devices without dropouts. Blue Moon IT commonly upgrades homes with UniFi, TP-Link Omada, or Eero systems to improve coverage and reliability.
Why Use a Guest Network in Your Home?
A guest network is more than a convenience—it's an important security layer.
Benefits of a Residential Guest Network
- Keeps visitors off your personal devices and data
- Protects IoT devices from potential intrusions
- Prevents accidental access to smart home controls
- Keeps family and guests on a separate bandwidth pool
Even smart devices that only need cloud access (smart plugs, some appliances, IoT sensors) can safely be placed on a guest network.
Commercial Wi-Fi: Choosing the Right Network Setup
Business environments have very different requirements from residential spaces. Workplaces often support:
This makes proper network separation and wireless planning critical.
When Businesses Should Use 2.4 GHz
Certain business devices rely on long-range, stable signals:
- EFTPOS terminals
- Barcode scanners
- Building sensors (temperature, humidity, occupancy)
- Industrial equipment
- Wireless printers (in larger spaces)
These systems typically use low-power radios compatible with 2.4 GHz.
When Businesses Should Use 5 GHz
Fast, interference-resistant Wi-Fi is essential for:
- Staff laptops and desktops
- Video conferencing systems
- VoIP phones and softphones
- Digital signage
- POS systems close to access points
- Staff smartphones and tablets
Businesses benefit greatly from multiple 5 GHz access points placed strategically around the site.
Why Guest Networks and VLANs Are Essential for Businesses
A commercial Wi-Fi deployment is incomplete without network segmentation.
Guest Network in a Business
A dedicated guest network:
- Keeps customers away from internal systems
- Protects company data
- Prevents malware spreading from guest devices
- Allows bandwidth limits and usage tracking
- Helps meet cybersecurity insurance requirements
Using VLANs for Additional Segmentation
Modern Wi-Fi systems allow the network to be divided into virtual LANs, such as:
This ensures each device type gets the access, speed, and protection it needs.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right Wi-Fi band and network structure dramatically improves performance, coverage, and security. Whether you're managing a family home full of smart devices or a business with hundreds of connections, using the correct mix of 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and guest networks creates a reliable and future-proof setup.
Key Takeaways:
- Use 2.4 GHz for IoT devices, smart home gadgets, and devices needing range over speed
- Use 5 GHz for high-bandwidth activities: streaming, gaming, video calls, and work devices
- Guest networks add essential security for both homes and businesses
- Most ISP routers cannot handle 25+ devices—consider mesh systems or additional access points
- Businesses should use VLANs to segment staff, guest, IoT, and payment networks
- Strategic access point placement is critical for commercial environments
- Network segmentation helps meet cybersecurity insurance requirements
